| [1]陈忠.主动脉血管疾病腔内治疗现状与展望[J].中华普通外科杂志,2015, 30(8):585-587.[2]陈忠,杨耀国. 胸主动脉夹层腔内修复术中封堵左锁骨下动脉的考量[J]. 中国血管外科杂志(电子版), 2016, 8(1):6-9.[3]陈纪言,罗淞元,刘媛. 急性主动脉夹层的腔内修复术治疗现状与展望[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2014, 29(1):1-3.[4]景在平,张荣杰,周建. 主动脉疾病腔内治疗的现状与展望[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2016, 31(8):617-619.[5]张龙江,祁吉. 对比剂肾病:一个值得关注的问题[J].中华放射学杂志, 2007,41(8):882-884.[6]El-Gamal EZA, Elmogy M, Atwan A. Current trends in medical image registration and fusion. Egypt Inform J. 2016;17(1):99-124.[7]Matl S,Brosig R,Baust M,et al. Vascular image registration techniques: a living review. Med Image Anal. 2017;35:1-17.[8]Vernikouskaya I, Rottbauer W, Seeger J, et al. Patient-specific registration of 3D CT angiography (CTA) with X-ray fluoroscopy for image fusion during transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) increases performance of the procedure. Clin Res Cardiol.2018:1-10.[9]Schulz CJ, Schmitt M, Böckler D, et al. Fusion imaging to support endovascular aneurysm repair using 3d-3d registration. J Endovasc Ther. 2016; 23(5):791-799.[10]Khalil A, Faisal A, Lai KW, et al. 2D to 3D fusion of echocardiography and cardiac CT for TAVR and TAVI image guidance. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2016; 55(8):1-10.[11]Ahmad W, Obeidi Y, Majd P, et al. The 2D-3D registration method in Image Fusion is accurate and helps to reduce the used contrast medium, radiation and procedural time in standard EVAR procedures. Ann Vasc Surg. 2018:177-186.[12]Koutouzi G, Sandström C, Roos H, et al. Orthogonal rings, fiducial markers, and overlay accuracy when image fusion is used for evar guidance. J Vasc Surg. 2016;52(5):604-611. [13]Izhar LI, Elamvazuthi I, Stathaki T, et al. Multimodal image registration for potential diagnosis and monitoring of morphoea using a hybrid NGC method// Int Conf Biomed Eng. 2017. [14]Chelbi S, Mekhmoukh A. Features based image registration using cross correlation and Radon transform. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2017:S1110016817302417. [15]Gouveia AR, Metz C, Freire L, et al. Registration-by-regression of coronary CTA and X-ray angiography. Comp Methods Biomech Biomed Eng Imaging Vis. 2017; 5(3):208-220.[16]Gouveia AR, Metz C, Freire L, et al. 3D-2D image registration by nonlinear regression. IEEE Int Sympos Biomed Imaging. 2012: 1343-1346.[17]Miao S , Wang ZJ , Liao R . A CNN Regression Approach for Real-Time 2D/3D Registration. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016; 35(5):1352-1363.[18]Miao S, Wang ZJ, Zheng Y, et al. Real-time 2D/3D registration via CNN regression. IEEE, Int Sympos Biomed Imaging. 2016:636-648.[19]Kendall A, Grimes M, Cipolla R. PoseNet: A Convolutional Network for Real-Time 6-DOF Camera Relocalization// IEEE Int Conf Comp Vis. 2015.[20]Hwang J, Park S, Kwak N. Athlete Pose Estimation by a Global-Local Network//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). IEEE, 2017.[21]Anjam SM, Banaee N, Rahmani H, et al. Determination of geometric accuracy of radiotherapy fields by port film and DRR using Matlab graphical user interface. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;(4):1-11.[22]Al-Qizwini M, Barjasteh I, Al-Qassab H, et al. Deep learning algorithm for autonomous driving using GoogLeNet// Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. 2017.[23]Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, et al. Going Deeper with Convolutions//2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, 2015.[24]雒培磊,李国庆,曾怡. 一种改进的基于深度学习的遥感影像拼接方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2017, 53(20):180-186.[25]Drusvyatskiy D, Lee HL, Ottaviani G, et al. The euclidean distance degree of orthogonally invariant matrix varieties. Israel J Math. 2017; 221(1):1-26.[26]Tong J, Zhao W, Lv H, et al. Transcriptomic profiling in human decidua of severe preeclampsia detected by RNA sequencing. J Cell Biochem. 2017;119(1):607-615.[27]Caiti G, Dobbe JGG, Strijkers GJ, et al. Positioning error of custom 3D-printed surgical guides for the radius: influence of fitting location and guide design. Int J Comp Assist Radiol Surg. 2018;13(4):507-518. [28]Ketcha MD, De ST, Han R, et al. Effects of Image Quality on the Fundamental Limits of Image Registration Accuracy. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2017;(99):1-1.[29]Ouadah S, Jacobson M, Stayman JW, et al. WE-AB-BRA-08: Correction of Patient Motion in C-Arm Cone-Beam CT Using 3D-2D Registration. Med Phys. 2016;43(6):3792-3793.[30]Hajirassouliha A, Taberner AJ, Nash MP, et al. Subpixel phase-based image registration using savitzky-golay differentiators in gradient-correlation. Comp Vis Image Understand. 2017.[31]Abolaban F, Zaman S, Cashmore J, et al. Changes in patterns of intensity-modulated radiotherapy verification and quality assurance in the UK. Clin Oncol. 2016;28(8):e28-e34. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
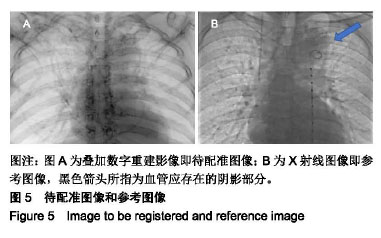
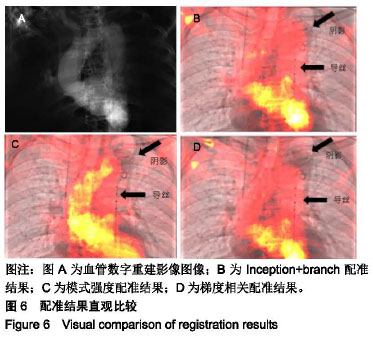
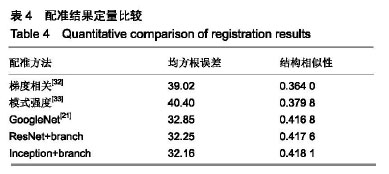
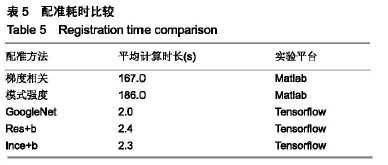
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
数字重建影像算法:是从射野方向或从类似模拟定位机的X射线靶方向观察3D重建影像的结果,目前多用于CT成像的3D到2D的投影。#br#
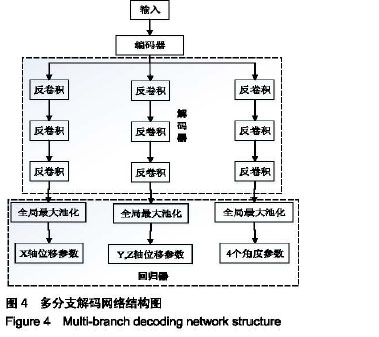
分支解码结构:在编码器输出之后,将解码器分成多股,以提高对不同任务的适应性。
#br#
文题释义:#br#
数字重建影像算法:是从射野方向或从类似模拟定位机的X射线靶方向观察3D重建影像的结果,目前多用于CT成像的3D到2D的投影。#br#
分支解码结构:在编码器输出之后,将解码器分成多股,以提高对不同任务的适应性。